7 Best Home Remedies for Fatty Liver: Natural Solutions for Liver Health

Table of Contents
Introduction to Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, particularly non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), has become increasingly prevalent in recent years. This condition occurs when excess fat accumulates in liver cells, potentially leading to inflammation, scarring, and even liver failure if left untreated. While conventional medicine offers various treatments, many people are turning to natural remedies to manage and reverse fatty liver disease.
As interest in holistic health approaches grows, more individuals are seeking guidance from qualified professionals who understand both conventional and natural healing methods. This is where Naturopathy Practitioner training comes into play, equipping practitioners with the knowledge to address complex health issues like fatty liver disease through natural means.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore seven effective home remedies for fatty liver, backed by scientific research and traditional wisdom. These natural solutions can complement conventional treatments and may help improve liver health, reduce inflammation, and support overall well-being.
1. Mediterranean Diet
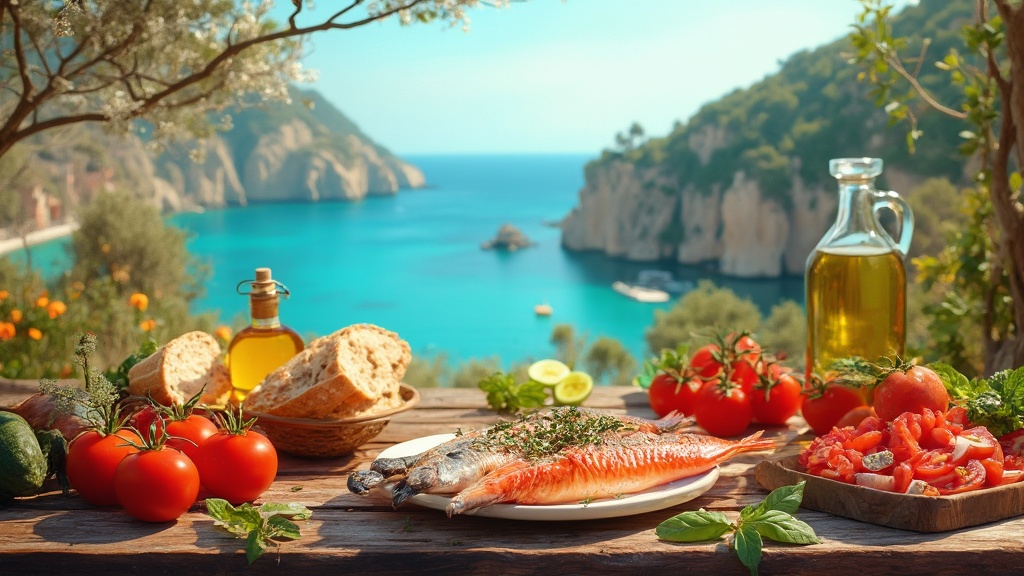

The Mediterranean diet has long been praised for its numerous health benefits, including its positive impact on liver health. This eating pattern emphasizes:
- Plenty of fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins, especially fish and poultry
- Healthy fats, particularly olive oil
- Limited red meat and processed foods
A study published in the Journal of Diabetes Spectrum highlighted the effectiveness of the Mediterranean diet in improving NAFLD and reducing cardiometabolic risks. The diet’s anti-inflammatory properties and high antioxidant content make it particularly beneficial for liver health.
To incorporate the Mediterranean diet into your lifestyle:
- Replace butter with olive oil in cooking and as a condiment
- Eat fish at least twice a week
- Include a variety of colorful vegetables in every meal
- Snack on nuts and seeds instead of processed snacks
- Limit red meat to once or twice a month
By adopting these dietary changes, you can significantly improve your liver health and overall well-being. For those interested in learning more about the role of nutrition in holistic health, the Introduction to Naturopathy course offers valuable insights into natural healing approaches.
2. Regular Exercise

Time Required: 30-60 minutes per day
Materials Needed: Comfortable clothing, supportive shoes, optional exercise equipment
Regular physical activity is crucial in managing fatty liver disease. Exercise helps reduce liver fat, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote overall metabolic health. The American Liver Foundation recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Effective exercises for fatty liver include:
- Brisk walking
- Jogging or running
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Strength training
A study featured in the PMC Journal found that regular exercise, combined with a healthy diet, significantly improved liver health in individuals with NAFLD. The research emphasized the importance of consistent physical activity in managing and potentially reversing fatty liver disease.
To incorporate more exercise into your routine:
- Start with short, manageable sessions and gradually increase duration and intensity
- Find activities you enjoy to make exercise more sustainable
- Consider joining group fitness classes or working with a personal trainer
- Use a fitness tracker to monitor your progress and stay motivated
- Incorporate movement throughout your day, such as taking the stairs or walking during lunch breaks
Benefits:
- Reduces liver fat accumulation
- Improves insulin sensitivity
- Enhances overall cardiovascular health
- Helps maintain a healthy weight
- Boosts mood and reduces stress, which can indirectly benefit liver health
Understanding the connection between physical activity and liver health is crucial for holistic well-being. Those interested in exploring this relationship further might find value in the naturopathy principles, practices, and benefits guide, which delves into the interconnectedness of physical activity and overall health.
3. Milk Thistle Supplementation
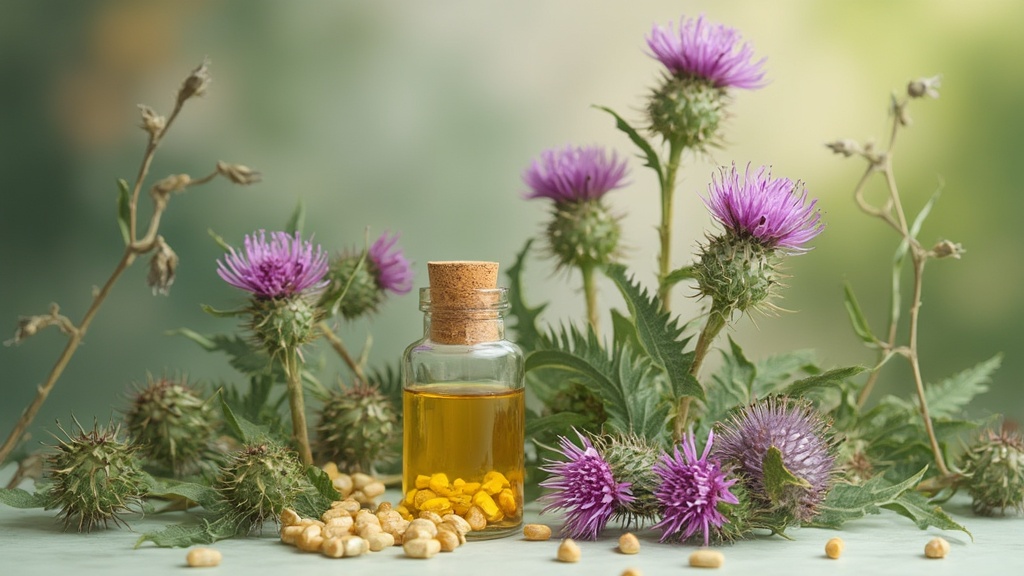

Milk thistle has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for liver ailments. Its active compound, silymarin, is known for its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, making it particularly beneficial for liver health.
Research published in the PMC Journal highlights milk thistle’s potential in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The study suggests that silymarin can help reduce liver inflammation, promote cell repair, and potentially improve liver function in individuals with NAFLD.
To incorporate milk thistle into your fatty liver management plan:
- Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific condition.
- Choose a high-quality milk thistle supplement from a reputable source.
- Consider taking milk thistle in capsule form or as a liquid extract.
- Be consistent with your supplementation, as benefits may take several weeks to become noticeable.
- Monitor your liver function tests regularly to track improvements.
It’s important to note that while milk thistle is generally considered safe, it can interact with certain medications. Always inform your healthcare provider about any supplements you’re taking.
| Milk Thistle Form | Typical Dosage | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Capsules | 200-400 mg, 2-3 times daily | Convenient, standardized dosage |
| Liquid Extract | 20-40 drops, 2-3 times daily | Faster absorption |
| Tea | 1-2 cups daily | Gentle, hydrating option |
For those interested in exploring natural remedies like milk thistle in more depth, the Naturopathy Practitioner Training Course offers comprehensive education on herbal medicines and their applications in various health conditions, including liver disorders.
4. Green Tea Extract

Green tea, particularly its concentrated extract form, has gained attention for its potential benefits in managing fatty liver disease. Rich in catechins, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), green tea extract offers powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that can support liver health.
A study published in the International Journal of Molecular Medicine found that green tea extract significantly reduced liver fat content and improved liver function in individuals with NAFLD. The research suggests that the catechins in green tea may help:
- Reduce liver fat accumulation
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Decrease oxidative stress in the liver
- Enhance overall liver function
To incorporate green tea extract into your fatty liver management plan:
- Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage.
- Choose a high-quality green tea extract supplement from a reputable source.
- Start with a lower dose and gradually increase to assess tolerance.
- Consider drinking 2-3 cups of green tea daily in addition to or instead of supplements.
- Be consistent with your intake, as benefits may take several weeks to become noticeable.
It’s important to note that while green tea is generally safe, high doses of green tea extract can potentially cause liver problems in some individuals. Always follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
For those interested in learning more about the therapeutic use of herbs and natural compounds, the beginner’s guide to naturopathy offers valuable insights into holistic approaches to health, including the use of natural remedies like green tea extract.
Case Study: The Corporate Wellness Initiative – Preventing Fatty Liver in the Workplace
A recent corporate wellness program implemented by a large tech company in Silicon Valley demonstrates the effectiveness of integrating natural remedies like green tea extract into employee health initiatives. The program, which included providing green tea and green tea extract supplements to employees, along with educational sessions on liver health, saw a 15% reduction in abnormal liver function tests among participants over a 6-month period.
This case study, highlighted by the American Liver Foundation’s Project Echo, underscores the potential of natural interventions in preventing and managing fatty liver disease in diverse populations.
5. Turmeric and Curcumin

Turmeric, a golden spice commonly used in Indian cuisine, has been revered for its medicinal properties for thousands of years. Its active compound, curcumin, is known for its powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, making it a promising natural remedy for fatty liver disease.
Research published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology suggests that curcumin may help:
- Reduce liver fat accumulation
- Decrease inflammation in the liver
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Protect liver cells from oxidative stress
To incorporate turmeric and curcumin into your fatty liver management plan:
- Add turmeric to your cooking, particularly in curries, soups, and smoothies.
- Consider taking a high-quality curcumin supplement, as it’s more concentrated than turmeric powder.
- Combine turmeric with black pepper to enhance absorption.
- Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific condition.
- Be patient and consistent, as benefits may take several weeks to become noticeable.
It’s worth noting that while turmeric is generally safe when used in cooking, high doses of curcumin supplements can interact with certain medications. Always inform your healthcare provider about any supplements you’re taking.
| Form of Turmeric/Curcumin | Typical Dosage | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Turmeric Powder | 1-3 grams daily | Cooking, teas |
| Curcumin Supplements | 500-2000 mg daily | Targeted therapeutic effects |
| Turmeric Tea | 1-2 cups daily | Gentle daily support |
For those interested in exploring the therapeutic potential of herbs like turmeric in more depth, the 10 naturopathic treatments for specific health conditions guide offers valuable insights into natural approaches to various health issues, including liver disorders.
6. Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), have shown promising results in managing fatty liver disease. These essential fats are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to improve lipid profiles, making them beneficial for liver health.
A study published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology found that omega-3 supplementation can help:
- Reduce liver fat content
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Decrease inflammation in the liver
- Enhance overall liver function
To incorporate omega-3 fatty acids into your fatty liver management plan:
- Include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines in your diet 2-3 times a week.
- Consider taking a high-quality fish oil or algae-based omega-3 supplement.
- Add plant-based sources of omega-3s like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts to your meals.
- Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific condition.
- Be consistent with your intake, as benefits may take several weeks to become noticeable.
It’s important to note that while omega-3 supplements are generally safe, they can interact with blood-thinning medications. Always inform your healthcare provider about any supplements you’re taking.
Case Study: Integrating Naturopathy for Fatty Liver Management
A recent case study from The Holistic Healing Clinic demonstrates the effectiveness of integrating omega-3 fatty acids in managing NAFLD. A 45-year-old male patient with diagnosed NAFLD showed significant improvements in liver enzyme levels and overall metabolic health after six months of following a comprehensive naturopathic treatment plan that included omega-3 supplementation.
This case study, highlighted by Crossroads Naturopathic, underscores the potential of natural interventions in managing fatty liver disease when combined with dietary modifications and lifestyle changes.
For those interested in learning more about the role of essential fatty acids in health and disease prevention, the naturopathy vs conventional medicine comparison offers valuable insights into how different medical approaches view and utilize nutritional therapies.
7. Weight Loss and Intermittent Fasting
Time Required: Varies; typically 16-hour fasting periods
Materials Needed: None specific; may use fasting apps for tracking
Weight loss and intermittent fasting have emerged as powerful tools in managing fatty liver disease. Even a modest weight reduction of 5-10% can significantly improve liver health in individuals with NAFLD. Intermittent fasting, a pattern of eating that alternates between periods of fasting and eating, has shown promising results in reducing liver fat and improving metabolic health.
A study published in the journal Cell Metabolism found that intermittent fasting can help:
- Reduce liver fat accumulation
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Enhance cellular repair processes
- Promote overall metabolic health
To incorporate weight loss and intermittent fasting into your fatty liver management plan:
- Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any weight loss or fasting regimen.
- Start with a modest calorie reduction and gradually increase as tolerated.
- Consider a 16/8 intermittent fasting schedule (16 hours fasting, 8 hours eating window).
- Focus on nutrient-dense, whole foods during eating periods.
- Stay hydrated during fasting periods.
It’s crucial to approach weight loss and intermittent fasting safely and under professional guidance, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Benefits:
- Significant reduction in liver fat content
- Improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control
- Enhanced cellular repair and autophagy
- Potential reversal of early-stage fatty liver disease
- Overall improvement in metabolic health markers
For those interested in exploring holistic approaches to weight management and metabolic health, the core principles of naturopathy guide offers valuable insights into natural methods for achieving and maintaining optimal health.
Conclusion
Managing fatty liver disease through natural remedies can be an effective complement to conventional treatments. By incorporating these seven home remedies – the Mediterranean diet, regular exercise, milk thistle supplementation, green tea extract, turmeric and curcumin, omega-3 fatty acids, and weight loss with intermittent fasting – you can take proactive steps towards improving your liver health.
It’s important to remember that while these natural approaches can be beneficial, they should be used in conjunction with professional medical advice. Every individual’s health situation is unique, and what works for one person may not be suitable for another. Always consult with a healthcare provider or a qualified naturopathic practitioner before making significant changes to your diet or starting new supplements.
Remember, the journey to optimal liver health is a holistic one that encompasses diet, lifestyle, and mindful interventions. By adopting these natural remedies and maintaining a balanced approach to health, you can support your liver function and promote overall wellness.
Explore More
- What Can You Do with a Naturopathy Certification?
- 7 Reasons to Become a Naturopathic Practitioner
- Dispelling Myths: Naturopathy is Not Pseudoscience, It is Evidence-Based Healing
- Integrating Naturopathy and Conventional Medicine
- Naturopathic Medicine in Women’s Health
- Getting Natural Relief from Pain Through Naturopathy








Responses